After decades of development, the foreign exchange (FX) market is now globally mature. Currency operations seem increasingly interesting for any Forex trader or Forex broker who wants to make his funds grow. The possibility to draw benefits in this market are endless, even when currency pairs start following a downtrend. Not all traders, however, gain opportunities in the Forex. Few investors, both institutional and private, manage to take advantage of reaping regular benefits in the FX.
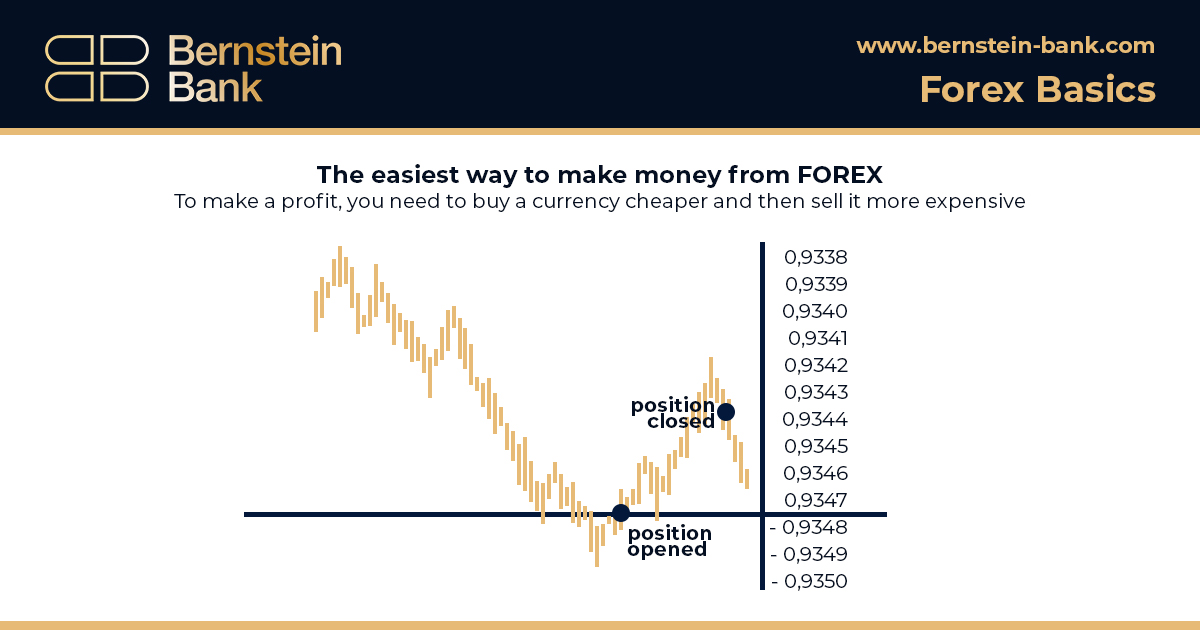
To make a profit, you need to buy a currency cheaper and then sell it more expensive or vice versa: sell more expensive and then buy cheaper. The size of the profit depends on the difference between the purchase price and the sale price. If you correctly predicted the direction of price movement, you make a profit, if wrong – the position will result in a loss.
Forex Intro
Forex or foreign-exchange market is a branch of a financial sector where convertible currencies are purchased and sold while respecting their rates of exchange that vary continuously. As a result of Internet’s globalization, the growing number of people want to take a chance in the currency market. Moreover, a lot of brokers allow you to benefit from tempting offers for a start. But how does the FX market actually function?
FX exists since March 1974 and allows traders to swap currencies the rates of which are in perpetual movement. It is available 24/5. The main global stock exchanges from Sydney to New York, via Frankfurt and London take turns to record cross-border transactions. Forex quotation always implies two currencies placed side by side; the one on the left is base currency and the right one is quotation currency or counterparty. Like in other financial markets, FX investors play on currency exchange rate variations to reap profits.
The majority of foreign exchange market transactions are carried out by swaps or by percentage rate swaps denominated in two different currency values. Over-the-counter and spot forward transactions are also present in the FX. Also, a good share of the activity in the Forex is ensured by banks and non-banking financial institutions.
Nearly 42% of exchanges take place between banks, 40% between a bank and a non-bank financial institution and 18% between a bank and a non-financial entity. Thousands of individuals also participate in trading investing through Forex platforms of banks or fund managers.
FX Pairs
There are several hundred currency pairs available on the foreign exchange market. The bulk of trading in the Forex, however, revolve around a handful of currencies, called major currencies. The pairs containing these currencies alone account for more than 95% of the daily exchanges that take place in the world.
US dollar heads the major global currencies, with the US currency capturing 86% of operations within the period of 2016-2018. The Euro is close behind, followed by Japanese yen, pound sterling, Swiss franc and Australian dollar. EUR/USD is the most widely traded asset for several years, with 24% market share in 2015. Apart from major currencies, the Forex hosts several other convertible currencies of less importance used by countries the economy of which occupies less space on the world stage. These assets are called exotic currencies, as much for their rarity on the market as for their unpredictability. The pairs containing these exotic currencies thus see their prices fluctuate at often unexpected amplitudes.
These values, even if they sometimes promise high returns remain reserved for experienced traders who realize the evolution of their costs.
