Global by nature, Forex market daily hosts millions upon millions of transactions across several currency pairs. What are these pairs? How to make a reasoned choice of currencies to work with Forex trading? How does an average Forex trader or Forex broker operate every day to gain income?
The foreign exchange (FX) qualifies, by definition, a finance industry, where investors purchase and distribute currencies in accordance with variances in the rates of exchange. Such an operation implies that the assets are to be sold in pairs. Thus, the price of each currency gets quoted subject to the price of another. The rate expressing this correlation is commonly named as exchange rate. There is, for instance, a EUR/USD pair, including Euro and US dollar. Each pair has a fluctuating cost which expresses the cost of purchasing and distributing a currency. Let us say, EUR/USD price is $1,12. This means that for 1€, you can have $1,12. The opposite is also true: to buy €1, you’ll need to pay $1,12. That is the way Forex works. With a Forex broker like Bernstein Bank you will be able to trade dozens of currency pairs. We are going to further examine that as with this operation one can release gains, and at the same time – lose money, as well.
Leverage in Forex trading
The concept of leverage is omnipresent. What is it exactly? Leverage is a mechanism that allows all Forex traders to take positions, whether buying or selling, significantly higher than the funds they have. It is a ratio that all brokers display on their trading platform.
Leverage varies from 2:1 to1000:1 in the FX market. In other words, with a leverage of 500:1, you have the option to take a position 500 times bigger than your actual capital. This mechanism allows you to reap larger profits, if you achieve good performance in Forex trading. In return, the leverage effect also generates significant losses in case of unfortunate decisions on the foreign exchange market.
A leverage effect is something variable. It will depend on several factors:
The regulator: Depending on the national or international law, leverage may be capped. However, this goes hand in hand with consumer protection.
Your broker: Depending on the chosen broker, leverage may be different.
Your investment strategy: It is also up to you to see how much leverage makes you feel comfortable.
As a general rule, a broker asks a trader for a minimal deposit and then gives him leverage. Imagine it totals to 50: 1. He wants to invest for €50 000 but only has €1000 to apply. With the deposit of €1000, a broker allows a trader to apply up to 50 times of his deposit (corresponding to leverage effect), i.e. €50 000. In this case, the earnings a trader makes will be credited to his account. Please note, losses should also be taken into account in a similar fashion.
In view of the risks of leveraging Forex trading, brokers set up a series of limitations aimed at minimizing losses, so that a trader does not lose more than he has on his account in case of losing trade. If this condition is not fulfilled, a broker makes a margin call, asking a trader to deposit the amount intended to cover his positions. If you trade with a broker liker Bernstein Bank, you will have full control over your position risk and margin requirement as you can set your stop-losses to the level you need and hence steer your margin requirements. Most brokers have minimal margin requirements. The requirements of large brokers range from 2% (or 50: 1) and 10% (10: 1) or more for minor currency pairs.
Leverage and Margin
Margin is calculated according to the leverage a trader’s account is set at. It is a sum of money that is engaged in a trade and blocked by a broker during the time of exposure on the market.
Trading without leverage (1:1)
To make it simple and understand what margin is, let us leave leverage aside for a moment and assume that we trade with 1:1 leverage (i.e. without it). For example, if you have $10,000 in your trading account and you buy EUR/USD for $5,000 (or 0.05 lots), how many dollars will you have to pay?
The EUR/USD currency pair is 1.12197. It means that a euro equals $1.12197. Therefore, without leverage (1:1) if you want to buy €5,000, you’ll have to pay $5609,85, because €5,000 = $5,000*$1.12197 = $5609,85.
If you buy EUR/USD for €5,000, you must have $5609,85 that will be mobilized by your broker to cover your position, it is this amount of $5609,85 which is called margin. If you close your position, this amount will be released by your Forex broker and you will no longer be exposed on the market.
Example with the leverage of 500: 1
Now assume that your trading account is 500:1 leverage. To buy €5,000, you will simply have to pay 1/500th or 0.002 of the amount you needed in the previous example, when you traded without leverage. To buy €5,000 you will need $5609,85*0.002 = $ 11,21. Only $11.21 needed as margin to invest €5,000 .
The leverage effect makes it possible to considerably increase the size of investments on financial markets. This characteristic of FX brokers offering CFD’s investment products explains their success, since they allow trading on the financial markets and profiting from them without heavy investment. Leverage, however, requires a lot of control, it is a double-edged sword that can multiply gains but can in parallel create significant financial losses.
Definition of pips, lot and spread
Getting started in Forex requires a minimum of knowledge and mastery of the basics of this market. Pips, lots and spreads are some of the must-know items in this area.
A pip: a standard unit of price variation
A pip is the smallest change in the price of a currency pair, which is able to be displayed on exchange platforms, and stock exchanges. By definition and by convention, a pip equals 1:1000, or 0,0001, regardless of the pair of currencies processed. Pips applied to parities, including Japanese yen, have an exception, because of the atypical nature of the Japanese currency. The pip used is 0.01 or 1:100, the ratio between the major currencies and yen often corresponding to a quotient of 100.
In general, Forex platforms set the rate of a lot at 100,000 units of the currency that is processed. There are, however, mini-lots consisting of 1,000 to 10,000 units of the currency being processed on the market. The main interest of lots is the ease with which they calculate the value of a pip for a given currency pair. Also, lots allow to quickly evaluating losses and gains on a currency trading.

Spread
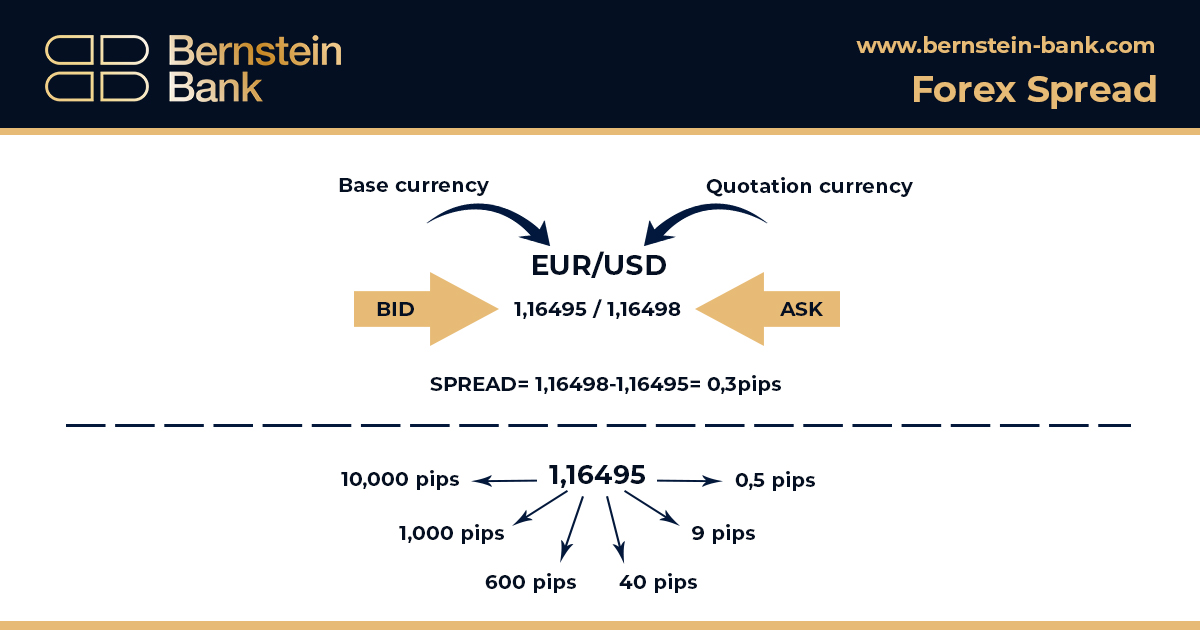
The spread concept is closely connected with the definition of pips. Specifically, spread determines the difference between the selling price and the purchase price of a currency, these prices being defined freely by a broker. Spread corresponds in this case to the transaction fees required by a broker. Spreads may be variable or fixed, depending on trading platforms.
On the trading platforms, spreads are represented by two prices placed side by side, for example EUR/USD: 1,2906/1,2909. The price on the left, or Bid, is the price with which a broker agrees to buy base currency from a trader. The price on the right, called Ask, is the price for which a broker agrees to sell the same base currency. Spread equals the difference between these two prices expressed in pips.